Introduction
3D laser scanners are transforming industries, from architecture to automotive design. Their precision and efficiency have redefined how we capture and analyze objects. But one question remains: how much does a 3D laser scanner cost?
In this article, we’ll explore the factors that influence the price of 3D laser scanners. We’ll also provide a guide to help you choose the right one for your needs.
Understanding 3D Laser Scanning Technology
What is a 3D Laser Scanner?
A 3D laser scanner is a non-contact, high-precision device used to capture the shape, dimensions, and surface details of objects or environments. The scanner emits laser beams that measure distances to the object's surface, creating a 3D point cloud—a digital representation of the scanned object. This data can be used to create accurate 3D models for applications in architecture, manufacturing, design, and beyond.
There are different types of 3D laser scanners, including those that use laser triangulation, structured light, or LiDAR technology. Each has its strengths and limitations, and the technology used can significantly impact the cost of the scanner.
Key Features of 3D Laser Scanners
The primary features that influence the cost of a 3D laser scanner are accuracy, speed, resolution, and range. High-quality scanners offer millimeter-level accuracy, fast scanning speeds, and high resolution, which are essential for projects requiring precision.
● Non-contact measurement: 3D laser scanners are ideal for scanning objects that cannot be touched or accessed directly, such as delicate artifacts or hazardous environments.
● High-speed scanning: The ability to scan millions of points per second allows for faster data collection and more efficient workflows.
● Precision and resolution: Scanners capable of high resolution capture fine details, which is crucial for reverse engineering or quality control in industrial applications.
Common Applications of 3D Laser Scanners
3D laser scanners are widely used in a variety of industries:
● Architecture: Capturing precise measurements of buildings and structures for renovation, restoration, or new construction projects.
● Manufacturing and Quality Control: Ensuring that parts and products meet specifications by scanning them for dimensional accuracy.
● Automotive and Aerospace Design: Using 3D scanning to capture complex shapes for reverse engineering, prototyping, and design modifications.
● Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: Scanning ancient artifacts and sites to create detailed records without causing damage.
Factors Influencing the Cost of a 3D Laser Scanner
Type of 3D Laser Scanner
The type of scanner you choose plays a significant role in its price. Handheld scanners are typically more affordable than stationary or industrial-grade scanners. Handheld scanners offer flexibility, allowing users to move freely around objects, which is ideal for smaller or more intricate scanning tasks.
On the other hand, stationary scanners are often used for larger-scale applications, such as building scans or industrial site documentation. These scanners are typically more expensive due to their high accuracy and ability to capture large volumes of data in a short time.
LiDAR-based scanners, which use laser pulses to measure distances and are often employed in geospatial applications, tend to be more expensive due to the advanced technology involved.
Accuracy, Resolution, and Scan Speed
The more precise and detailed the scan, the higher the cost. Professional-grade 3D laser scanners often offer sub-millimeter accuracy, which is crucial for industries such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing, where even the slightest margin of error can be costly. Higher resolution allows for more detailed models, which is particularly useful for tasks like reverse engineering.
Scan speed also plays a critical role in pricing. Faster scanners can capture more points in less time, making them ideal for large-scale scans or projects with tight deadlines. However, faster scanners may come with a higher price tag due to the technology required to process large datasets quickly.
Additional Features and Capabilities
Some 3D laser scanners come with additional features that add value but also increase the cost. These include:
● Software compatibility: High-end scanners often come with proprietary software or are compatible with industry-standard software, such as CAD tools, which can drive up costs.
● Portability: Handheld, lightweight models are often more expensive due to their compact design and flexibility.
● Ergonomic design: For ease of use, many modern scanners offer user-friendly interfaces, intuitive controls, and comfortable ergonomics, which also affect the price.
Feature | Description | Impact on Cost |
Non-Contact Measurement | Scans without physical contact, reducing risk of damage | Essential for delicate objects, increases price |
High-Speed Scanning | Faster data capture speeds for large projects | More expensive models offer high speeds |
CAD Software Integration | Compatibility with design software | Adds value but increases cost due to software requirements |
Portability | Handheld models for on-the-go scanning | Adds cost due to compact design |
Price Range of 3D Laser Scanners
Low-Cost Options
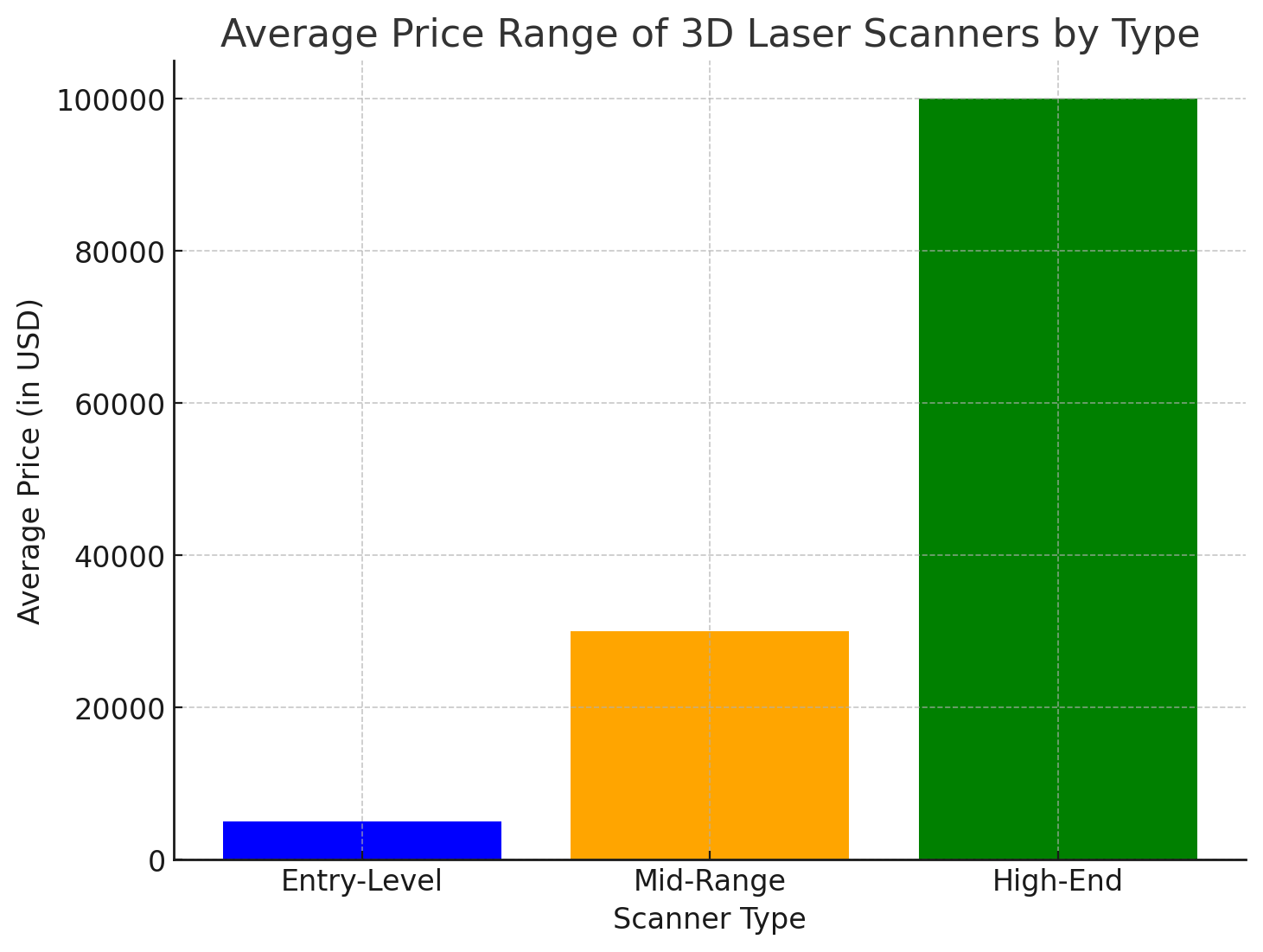
Entry-level 3D laser scanners designed for hobbyists, small businesses, or educational purposes can cost as little as $500 to $5,000. These scanners are generally less accurate and offer lower resolution, making them suitable for non-professional applications like prototyping or basic design.
While affordable, these scanners may not meet the needs of industries requiring high precision and reliability. Users should consider the trade-off between cost and performance, especially if the scanner will be used for professional or commercial purposes.
Mid-Range Scanners
Professional 3D laser scanners, which offer a balance of accuracy, resolution, and speed, typically range from $10,000 to $50,000. These models are ideal for businesses that need reliable scanning for tasks like design, quality control, or reverse engineering, but don’t require the highest possible accuracy.
Mid-range scanners are popular in industries like construction, automotive design, and product development. They provide sufficient accuracy for most general-purpose applications, while still being affordable for small to medium-sized enterprises.
High-End, Professional-Grade Scanners
At the high end of the market, 3D laser scanners can exceed $100,000. These scanners are typically used for industrial, metrology-grade applications, where extreme precision is necessary. They are ideal for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where accuracy is paramount.
High-end scanners often come with advanced features like LiDAR technology, long-range scanning, and the ability to handle complex environments. They are typically used in large-scale projects or applications that require high-quality data and analysis.
Scanner Type | Price Range | Ideal Use Case |
Entry-Level 3D Scanner | $500 - $5,000 | Hobbyists, small businesses, educational use |
Mid-Range Scanner | $10,000 - $50,000 | Professional use in design, quality control |
High-End 3D Scanner | $100,000 and above | Industrial applications, high-precision needs |
Renting vs. Purchasing a 3D Laser Scanner
When to Rent a 3D Laser Scanner
Renting a 3D laser scanner can be a cost-effective solution for short-term projects or when only occasional use is required. Rental prices typically range from $500 to $3,000 per day, depending on the scanner's model and features.
Renting is a good option for businesses that need a scanner for a specific project but do not have the budget or need for a long-term investment. It also allows users to access high-end equipment that they might not otherwise be able to afford.
When to Buy a 3D Laser Scanner
For companies with ongoing scanning needs, purchasing a 3D laser scanner can be more economical in the long run. Although the upfront cost can be high, owning a scanner eliminates rental fees and gives businesses the flexibility to scan whenever needed. Additionally, owning a scanner can provide access to regular updates, training, and support.
Buying a 3D laser scanner also ensures that the equipment is calibrated to the user's specific needs, which may be critical for industries requiring high levels of precision.
Aspect | Renting | Purchasing |
Upfront Cost | Low (daily/weekly rental fees) | High (full price of the scanner) |
Long-Term Cost | Can become expensive over time | More cost-effective in the long run |
Flexibility | Ideal for short-term use | Best for long-term or frequent use |
Maintenance and Support | Included in rental fee | Requires additional maintenance costs |
Hidden Costs of 3D Laser Scanning
Software and Post-Processing Costs
In addition to the scanner itself, there are often hidden costs associated with 3D laser scanning. Most high-end scanners require specialized software for data processing, modeling, and analysis. Software licenses can cost anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand dollars annually, depending on the tools and features needed.
Post-processing is also a significant cost factor, particularly for detailed models. Complex data may require more time and specialized software to convert it into usable formats like CAD models or 3D meshes.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to ensure that the 3D laser scanner continues to operate at peak performance. Over time, wear and tear can affect the scanner’s accuracy, requiring costly repairs or recalibration. For industries where precision is critical, these ongoing costs should be considered when budgeting for a 3D laser scanner.
How to Choose the Right 3D Laser Scanner for Your Needs
Assessing Your Project Requirements
When selecting a 3D laser scanner, it’s crucial to assess the size, complexity, and precision requirements of your projects. Larger objects, such as buildings or industrial sites, may require more powerful, stationary scanners. Conversely, smaller or more intricate objects may be better suited to handheld models.
Additionally, consider the environmental factors where the scanner will be used, such as temperature, humidity, or the need for portability.
Matching Budget with Capabilities
It’s important to balance the scanner's capabilities with your budget. While high-end scanners offer exceptional precision, they may be overkill for many applications. For general-purpose use, mid-range models may provide the best value, offering the necessary accuracy without the steep price tag.
Importance of Vendor Support and Service
Before purchasing or renting a 3D laser scanner, it’s essential to consider the support and service options provided by the vendor. High-quality customer service, training, and maintenance options can make a significant difference in ensuring the scanner performs well over time.

Conclusion
The cost of a 3D laser scanner varies based on factors like type, features, and project needs. Understanding these elements helps you choose the right scanner, whether renting or purchasing. By aligning your budget with the capabilities you require, you can ensure long-term value. ZG Technology offers high-quality 3D scanning solutions, providing precision and efficiency for businesses looking to upgrade their equipment and streamline operations.
FAQ
Q: How much does a 3D laser scanner cost?
A: The cost of a 3D laser scanner varies widely based on type, features, and precision. Entry-level models can start around $500, while high-end models for industrial applications may exceed $100,000.
Q: What factors affect the cost of a 3D laser scanner?
A: Factors influencing the cost of a 3D laser scanner include its accuracy, scan speed, resolution, and additional features like software compatibility and portability.
Q: Should I rent or buy a 3D laser scanner?
A: Renting is ideal for short-term projects, while purchasing is better for long-term use. The decision depends on your project's scale and frequency of use.
Q: Why are some 3D laser scanners so expensive?
A: High-end 3D laser scanners offer advanced features, such as metrology-grade accuracy, longer range, and faster scan speeds, which contribute to their higher cost.
Q: What are the advantages of using a 3D laser scanner in business?
A: A 3D laser scanner provides high precision and efficiency, making it essential for applications like quality control, design, and reverse engineering. It reduces manual labor and errors.
Q: How do I choose the right 3D laser scanner for my needs?
A: Consider factors like the size and complexity of your projects, required accuracy, and budget. Match your specific needs to a scanner's capabilities for the best value.



