Introduction
LiDAR technology has transformed industries like autonomous vehicles and mapping. As new advancements emerge, 4D LiDAR is gaining attention.
In this article, we'll compare 3D LiDAR and 4D LiDAR, highlighting their differences and key applications. You’ll learn about their respective advantages, limitations, and how to choose the right solution for your needs.
What is 3D LiDAR?
How 3D LiDAR Works
3D LiDAR works by emitting laser pulses that bounce off objects and return to the sensor. By measuring the time it takes for the pulse to return, the system can determine the distance to objects in the surrounding environment. This process is known as Time of Flight (ToF) technology. With this technology, 3D LiDAR systems generate a "point cloud," a digital representation of the environment, capturing detailed 3D maps. The accuracy and resolution of the data depend on the density of the point cloud and the number of laser channels the sensor has.
Advantages of 3D LiDAR
3D LiDAR offers remarkable precision in creating highly accurate distance measurements, making it ideal for applications like geographic mapping, construction, and autonomous vehicles. It is widely used in autonomous vehicles for real-time mapping and object detection. Since 3D LiDAR systems are well-established, they tend to be more cost-effective compared to newer technologies. Additionally, it provides high resolution and accuracy in scenarios where dynamic object tracking is not critical.
Limitations of 3D LiDAR
While 3D LiDAR is excellent at mapping static objects, it does not provide information about the velocity of objects or moving targets. This limitation becomes apparent in fast-moving environments like autonomous driving, where detecting the speed and direction of moving objects is crucial. Furthermore, 3D LiDAR systems can struggle in adverse weather conditions such as heavy rain or fog. The light pulses scattered in these conditions can result in data loss, reducing the overall effectiveness of the system.
Technology | Advantages | Limitations |
3D LiDAR | - High accuracy for stationary objects | - Cannot track moving objects |
| - Well-established and cost-effective | - Performance reduces in adverse weather |
4D LiDAR | - Real-time velocity and motion tracking | - More expensive |
| - Improved performance in dynamic environments | - Steeper learning curve for integration |

What is 4D LiDAR?
How 4D LiDAR Works
4D LiDAR builds upon the capabilities of 3D LiDAR by introducing an additional dimension: velocity. This is achieved through the Doppler effect, which measures the frequency shift in laser light as it reflects off moving objects. In essence, 4D LiDAR systems are capable of detecting not only the distance of objects but also their speed and direction. By combining these three elements—distance, direction, and velocity—4D LiDAR enables real-time motion detection, making it invaluable in dynamic environments.
Advantages of 4D LiDAR
The major advantage of 4D LiDAR over 3D LiDAR is its ability to capture dynamic information about the environment. This is particularly valuable in applications like autonomous vehicles, where real-time tracking of moving objects is necessary. For instance, 4D LiDAR can track vehicles, pedestrians, or cyclists and provide real-time updates on their speed and movement. This additional dimension makes 4D LiDAR ideal for complex environments with high-speed motion, such as city streets or highways. It can also perform better in conditions where motion detection is critical, offering more comprehensive data compared to 3D LiDAR.
Limitations of 4D LiDAR
While 4D LiDAR offers more advanced capabilities, it comes with certain challenges. The technology is still relatively new and often comes with a higher cost due to its complexity and the advanced features it offers. Additionally, integrating 4D LiDAR systems can require more specialized knowledge and training, leading to a steeper learning curve. Despite these drawbacks, the ability to capture both the spatial and temporal aspects of an environment makes 4D LiDAR a powerful tool in many high-speed, real-time applications.
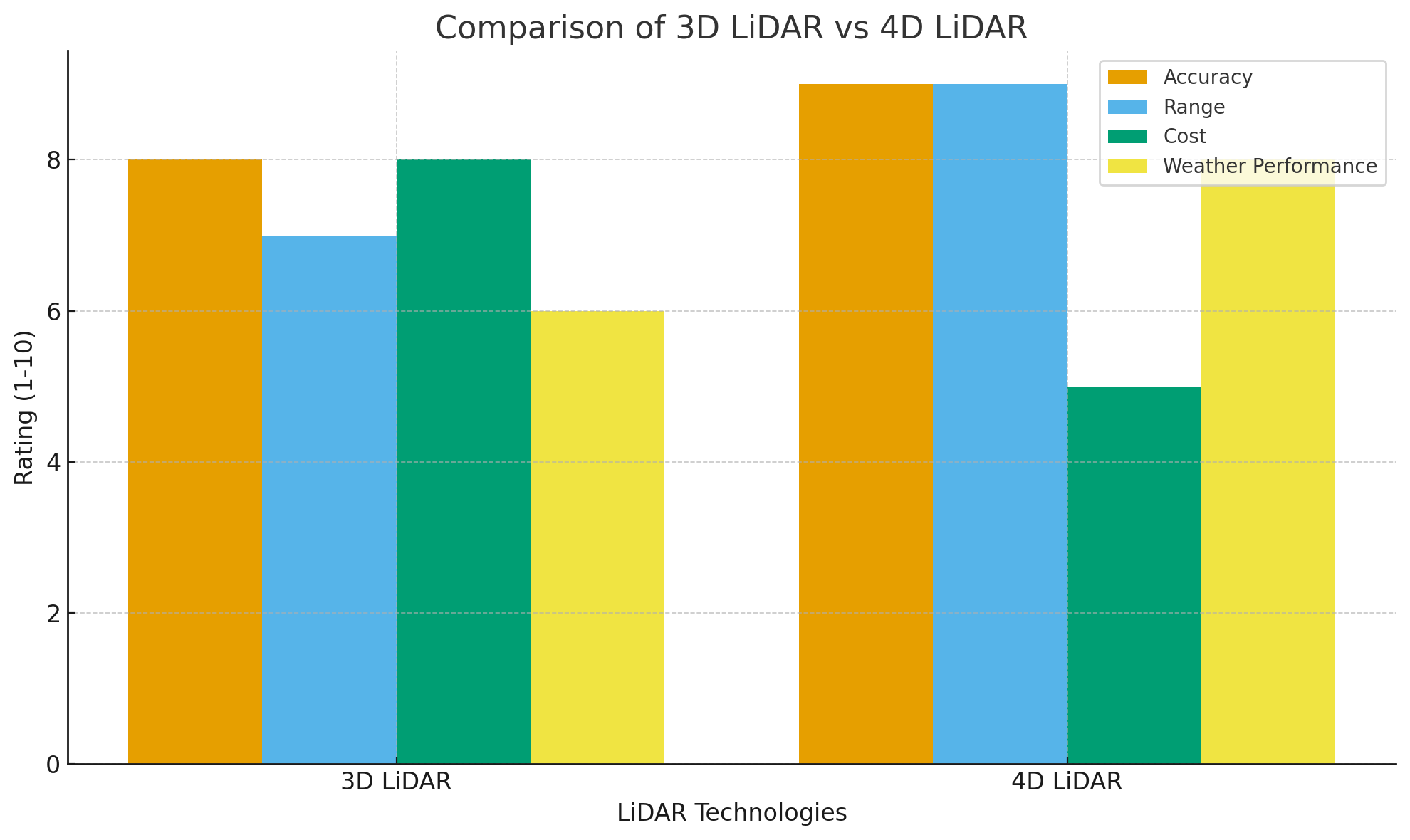
3D LiDAR vs 4D LiDAR: A Detailed Comparison
Accuracy and Resolution
Both 3D LiDAR and 4D LiDAR offer high-resolution data, but their applications differ. 3D LiDAR excels at creating precise 3D maps of static environments. It is particularly effective in scenarios where the primary need is high spatial accuracy, such as in architectural modeling or environmental mapping. On the other hand, 4D LiDAR provides similar resolution but with the added benefit of velocity detection. This extra layer of data makes 4D LiDAR particularly useful for dynamic environments where understanding the movement of objects is critical, such as in autonomous driving.
Range and Speed
3D LiDAR typically has a shorter range compared to 4D LiDAR. This makes 3D LiDAR ideal for applications that require high precision over smaller distances, such as mapping buildings or structures. However, 4D LiDAR is designed for longer-range detection, making it more suitable for high-speed applications. For example, in autonomous vehicles, 4D LiDAR can detect objects at a greater distance and track their movement, which is essential for ensuring safety at high speeds.
Environmental Performance
3D LiDAR struggles in adverse weather conditions such as fog, rain, or snow, where light-based systems may not perform optimally due to light scattering. In contrast, 4D LiDAR's ability to detect motion in real-time adds an additional layer of robustness, particularly in challenging environments. Although it still relies on light pulses, the incorporation of velocity measurement helps maintain reliability even in environments with moving objects, making it a more versatile option for dynamic conditions.
Cost and Integration
3D LiDAR systems are generally more affordable and easier to integrate into existing workflows, as they have been around longer and are well-established in various industries. In comparison, 4D LiDAR systems tend to be more expensive due to their advanced capabilities. The increased cost of 4D LiDAR may be a deterrent for some organizations, but the enhanced data quality it provides in high-speed or dynamic scenarios may justify the investment for certain use cases.
Feature | 3D LiDAR | 4D LiDAR |
Data Type | 3D point clouds (spatial) | 3D point clouds + velocity (dynamic) |
Accuracy | High accuracy for stationary objects | High accuracy for dynamic and moving objects |
Range | Short to medium distances | Longer detection range |
Cost | More affordable | Higher cost due to advanced features |
Application Areas | Environmental mapping, construction | Autonomous driving, real-time tracking |
Weather Performance | Struggles in poor weather | Better performance in dynamic environments |
When to Choose 3D LiDAR
Suitable Applications for 3D LiDAR
3D LiDAR is an excellent choice for applications where precision and accuracy over short to medium distances are required. It is widely used in environmental mapping, such as surveying forests, parks, or large building projects. It is also ideal for situations where the focus is on static objects, such as creating 3D models of buildings, infrastructure, or historical sites.
Why 3D LiDAR is Still a Preferred Option
Despite the advancements in 4D LiDAR, 3D LiDAR remains a reliable and cost-effective solution for many industries. Its established presence in the market and affordability make it the go-to choice for applications that do not require real-time velocity tracking. For tasks like creating topographic maps or architectural designs, 3D LiDAR remains highly effective.
When to Choose 4D LiDAR
Suitable Applications for 4D LiDAR
4D LiDAR is best suited for dynamic environments, particularly where objects are in motion. This makes it a key technology for autonomous vehicles, where both distance and velocity must be continuously monitored. It is also beneficial in robotics, industrial automation, and real-time monitoring systems, where motion tracking is essential for precise control and navigation.
The Edge of 4D LiDAR in Emerging Technologies
4D LiDAR is at the forefront of emerging technologies, particularly in sectors like autonomous transportation, robotics, and real-time data processing. Its ability to provide velocity data alongside spatial measurements positions it as a critical tool for future innovations in autonomous driving, advanced robotics, and environmental monitoring.
Scenario | 3D LiDAR | 4D LiDAR |
High precision over short distances | Ideal for mapping small areas | Less relevant due to long-range focus |
Tracking moving objects | Not suitable for dynamic tracking | Ideal for real-time object tracking |
Cost-sensitive applications | More affordable | Higher cost, but advanced features |
Autonomous vehicles | Limited to static mapping | Essential for dynamic tracking |
Conclusion
The choice between 3D LiDAR and 4D LiDAR depends on the application’s specific needs. 3D LiDAR is ideal for high-accuracy tasks over short to medium distances, while 4D LiDAR excels in dynamic environments where velocity tracking is essential. Both have their advantages, and choosing the right one depends on factors like range, precision, and cost. ZG TECHNOLOGY provides advanced LiDAR solutions that meet various industry needs, offering high performance and efficiency for projects.
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between 3D LiDAR and 4D LiDAR?
A: The main difference is that 3D LiDAR provides spatial data, creating detailed 3D maps, while 4D LiDAR adds velocity measurements, enabling real-time tracking of moving objects.
Q: How does a 3D Laser Scanner work?
A: A 3D Laser Scanner uses laser pulses to create detailed point clouds, measuring distances accurately to generate 3D models. It’s widely used in construction and mapping.
Q: When should I choose 4D LiDAR over 3D LiDAR?
A: 4D LiDAR is ideal for environments where tracking velocity and movement in real-time is crucial, such as autonomous vehicles or high-speed robotics.
Q: Is 4D LiDAR more expensive than 3D LiDAR?
A: Yes, 4D LiDAR tends to be more expensive due to its advanced features, including velocity measurement and real-time dynamic tracking.
Q: Can I use a 3D Laser Scanner for autonomous vehicle applications?
A: While 3D Laser Scanners are accurate for static mapping, 4D LiDAR is more suitable for autonomous vehicles due to its ability to track moving objects.
Q: What are the advantages of 4D LiDAR?
A: 4D LiDAR provides enhanced capabilities, including real-time motion detection and velocity tracking, making it ideal for dynamic and high-speed applications.
Q: How accurate is a 3D Laser Scanner?
A: A 3D Laser Scanner is highly accurate, providing precise measurements for creating detailed 3D models in various applications, from construction to environmental mapping.



